Single Linked list
我們先實作一個簡單的 linked list,我們使用 main.c 來撰寫主要的測試 case , list.h 來定義 linked list 的結構和函式原型, list.c 來實作 linked list 的函式。完整的程式可以參考 code。
本篇範例程式在 GitHub - sigle linked list
實作 linked list 的新增、刪除
先建立以下檔案:
.
├── list.c
├── list.h
└── main.c
main.c:主要的程式入口
在 main.c 中,我們會先撰寫整個程式的主要邏輯跟所需要的函式。這裡我們使用 dummy head node 來簡化 linked list 的操作,這樣可以避免處理空 linked list 的情況。
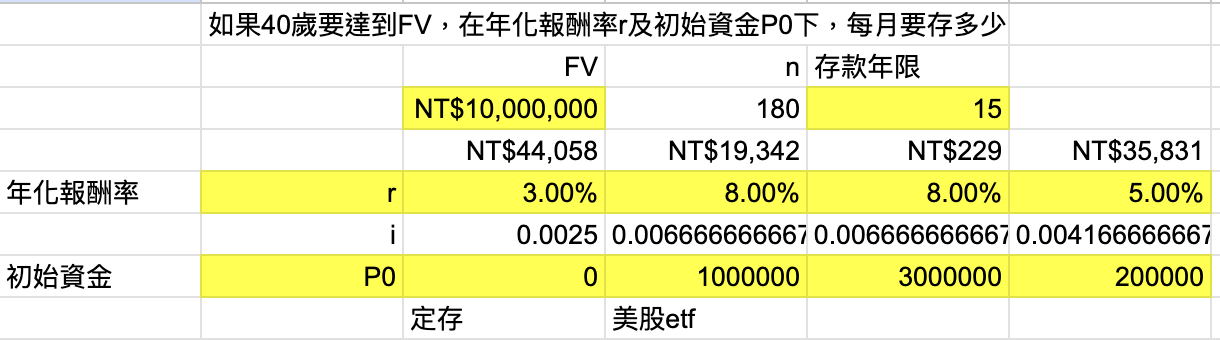
資訊
由以下圖可知,如果沒有 dummy head node,當 linked list 為空時,head 會指向 NULL,這樣在插入或刪除節點時需要特別處理空 linked list 的情況。而有了 dummy head node 後,head 永遠不會是 NULL,這樣就可以簡化程式碼。
A. 沒有 dummy B. 有 dummy
┌────┐ ┌────┐ ┌────┐ ┌────┐ ┌────┐ ┌────┐
│ 1 │──▶ │ 2 │──▶ │ 3 │ │ D │──▶ │ 1 │──▶ │ 2 │──▶ │ 3 │
└────┘ └────┘ └────┘ └────┘ └────┘ └────┘
head head(固定指向 D)
int main()
{
Node *head = create_node(-1); // create a dummy head node
// create a linked list with 5 nodes
// insert 5 nodes at the tail
for (int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
insert_tail(head, i);
}
print_list(head);
// insert 5 nodes at the head
for (int i=5; i<10; i++)
{
insert_head(head, i);
}
print_list(head);
// delete the specific node with value 3
delete_node(head, 3);
print_list(head);
// delete the middle node
delete_mid(head);
print_list(head);
free_list(head);
// delete the duplicate nodes
head = create_node(-1);
for (int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
for (int j=0; j<2; j++) {
insert_tail(head, i);
}
}
print_list(head);
delete_dup(head);
print_list(head);
return 0;
}
在 list.h 定義的結構和函式原型:
typedef struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
} Node;
Node* create_node(int n);
void free_list(Node *node);
void print_list(Node *node);
void insert_tail(Node *node, int n);
void insert_head(Node *node, int n);
void delete_node(Node *node, int n);
void delete_head(Node *node);
void delete_tail(Node *node);
void delete_mid(Node *node);
void delete_dup(Node *node);
list.c 基本的建立節點及結構
宣告 Node 結構,在 list.h 中定義 linked list 的節點結構,包含 data 和 next 指標。
typedef struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
} Node;
建立節點
Node* create_node(int n)
{
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node->data = n;
node->next = NULL;
return node;
}
在 list.c 實作新增到尾
先找到 linked list 的尾端,然後將新的節點插入到尾端。
void insert_tail(Node* node, int n)
{
// 找到 linked list 的尾端
while (node->next != NULL)
{
node = node->next;
}
// 在尾端插入新的節點
node->next = create_node(n);
}
在 list.c 實作新增到頭
void insert_head(Node* dummy, int value)
{
printf("insert head %d\n", value);
Node* new_node = create_node(value); // 建立新節點
new_node->next = dummy->next; // 指向原本第一個節點
dummy->next = new_node; // dummy 指向新的第一個節點
}
實作刪除特定節點
void delete_node(Node* node, int n)
{
printf("delete node %d\n", n);
Node* pre = node;
node = node->next; // 跳過 dummy head
while (node!=NULL)
{
// 如果找到要刪除的節點
if (node->data==n) {
pre->next = node->next;
free(node);
return;
}
// 如果沒有找到,繼續往下走
pre = node;
node = node->next;
}
}
實作刪除中間節點
刪除中間節點,我們可以使用 fast-slow pointer 的方法來找到中間節點。
void delete_mid(Node* head)
{
if (!head || !head->next || !head->next->next) return;
puts("delete mid");
Node* slow = head->next; // 跳過 dummy head
Node* fast = head->next; // 跳過 dummy head
Node* pre = head;
while (fast && fast->next)
{
pre = slow;
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
// 如果 slow 為 NULL,表示鏈表長度為 1 或 0,無需刪除
if (slow) {
pre->next = slow->next;
free(slow);
}
}
實作刪除重複節點
void delete_dup(Node *head)
{
if (!head)
return;
Node *current = head; /* dummy head 假設存在 */
Node *next = head->next;
while (next) {
if (current->data == next->data) {
Node *dup_next = next->next;
current->next = dup_next;
free(next); /* 直接釋放重複節點 */
next = dup_next; /* 不移動 current,繼續檢查 */
} else {
current = next;
next = next->next;
}
}
}
實作交換 a、b 節點
void swap(Node *head, int a, int b)
{
puts("swap");
if (a == b || !head || !head->next)
return;
/* 1. 找到 a、b 的前驅與本身 */
Node* iter = head; /* 從 dummy 開始 */
Node* prevA = NULL; /* a 的前驅 */
Node* prevB = NULL; /* b 的前驅 */
Node* currA = NULL; /* a 的本身 */
Node* currB = NULL; /* b 的本身 */
while (iter) {
if (iter->data == a) {
currA = iter; /* 找到 a */
if (!prevA) /* 若 prevA 還沒找到,則記錄前驅 */
prevA = head; /* dummy head */
} else if (iter->data == b) {
currB = iter; /* 找到 b */
if (!prevB) /* 若 prevB 還沒找到,則記錄前驅 */
prevB = head; /* dummy head */
}
if (currA && currB) /* 都找到了就可以退出迴圈 */
break;
iter = iter->next;
}
/* 2. 其中一個沒找到就退出 */
if (!currA || !currB)
return;
/* 3. 若 a、b 相鄰,需要特別分左右兩種情況 */
if (currA->next == currB) { /* A 在 B 前 */
prevA->next = currB;
currA->next = currB->next;
currB->next = currA;
} else if (currB->next == currA) { /* B 在 A 前 */
prevB->next = currA;
currB->next = currA->next;
currA->next = currB;
} else { /* 不相鄰 */
/* 4. 一般情況:交換前驅的 next,再交換兩節點的 next */
prevA->next = currB;
prevB->next = currA;
Node *tmp = currA->next;
currA->next = currB->next;
currB->next = tmp;
}
}
實作反轉 linked list
void reverse(Node *head)
{
puts("reverse");
/* 1. 判空:若只有 dummy,直接返回 */
if (!head || !head->next || !head->next->next)
return;
Node *prev = NULL; /* 已反轉部分的第一節點(翻轉後是尾) */
Node *curr = head->next; /* 目前掃描到的節點(待反轉) */
Node *next = NULL; /* 暫存 curr->next,防止指標失效 */
while (curr) {
next = curr->next; /* 2. 暫存下一節點 */
curr->next = prev; /* 3. 反轉指向 */
prev = curr; /* 4. prev 前進 */
curr = next; /* 5. curr 前進 */
}
/* 6. 迴圈結束時 prev 指向反轉後的新鏈首,把 dummy 指向它 */
head->next = prev;
}
實作反轉 K 個節點
/* 以 dummy 為鏈首,將串列每 k 個節點反轉 */
void reverseK(Node *dummy, int k) {
puts("reverseK");
if (k <= 1 || !dummy || !dummy->next) return;
Node *group_prev = dummy; /* 目前這組前一個節點(首輪為 dummy) */
while (1) {
/* 1️⃣ 找到這組第 k 個節點 (kth) */
Node *kth = group_prev;
for (int i = 0; i < k && kth; ++i)
kth = kth->next;
if (!kth) break; /* 剩餘不足 k 個,不反轉 */
Node *group_next = kth->next; /* 下一組開頭 */
/* 2️⃣ 就地反轉 [group_prev->next, kth] 之間的指標 */
Node *prev = group_next;
Node *curr = group_prev->next;
while (curr != group_next) {
Node *tmp = curr->next;
curr->next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = tmp;
}
/* 3️⃣ 接回前後串列 */
Node *old_group_head = group_prev->next;
group_prev->next = kth;
group_prev = old_group_head; /* 為下一輪準備:此時它是反轉後的尾 */
}
}
實作 merge sort linked list
// Merge two sorted lists using comparator
Node* merge(Node *a, Node *b, int (*cmp)(int, int)) {
Node dummy;
Node *tail = &dummy;
dummy.next = NULL;
while (a && b) {
if (cmp(a->data, b->data) <= 0) {
tail->next = a; // 接上較小的節點
a = a->next;
} else {
tail->next = b;
b = b->next;
}
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = a ? a : b; // 接上剩餘的節點
return dummy.next;
}
// Helper: merge sort for linked list with comparator
static Node* merge_sort_internal(Node* head, int (*cmp)(int, int)) {
if (!head || !head->next) return head;
Node *slow = head, *fast = head->next;
while (fast && fast->next) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
Node *mid = slow->next;
slow->next = NULL;
Node *left = merge_sort_internal(head, cmp);
Node *right = merge_sort_internal(mid, cmp);
return merge(left, right, cmp);
}
// Sort using merge sort with comparator function
void sort(Node *node, int (*cmp)(int, int)) {
node->next = merge_sort_internal(node->next, cmp);
}
// Convenience: ascending order comparator
int cmp_asc(int a, int b) { return a - b; }
// Convenience: descending order comparator
int cmp_desc(int a, int b) { return b - a; }
編譯
gcc -Wall -o linked_list.out main.c list.c
-Wall參數會開啟所有警告訊息,這樣可以幫助我們在編譯時發現潛在的問題。-o linked_list.out參數指定輸出的可執行檔名稱為linked_list.out。gcc是 GNU C Compiler 的縮寫,是一個開源的 C 語言編譯器。 會產生linked_list.out可執行檔。
執行
$ ./linked_list.out
-1 0 1 2 3 4
TODO remove_head remove_tail delete_mid delete_dup swap reverse reverseK sort ascend descend merge